The Bladder, located in the Lower abdomen, connects through the ureters at the upper end with the Kidneys, and at the Lower end with the urethra. Since the Bladder and Shen Meridians connect with each other, they are externally–internally related. The Bladder stores and discharges urine. The Basic Questions says, “The Bladder is like a district official; it stores the fluids so that they can be excreted by its Qi transformation”. The Qi transformation of Shen produces urine from spent or surplus body fluid, stores it in the Bladder, and discharges it through the urethra. Some Bladder disorders are affected by disordered Qi transformation of Shen.
The physiological functions of the bladder
(1) The bladder relates to Shen
Shen 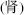 and the Bladder connect externally–internally via their meridians. The Qi transformation of Shen
and the Bladder connect externally–internally via their meridians. The Qi transformation of Shen 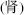 prompts the Bladder to store and excrete urine. Insufficient Shen
prompts the Bladder to store and excrete urine. Insufficient Shen 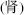 –Qi, with subsequent failed Bladder control, presents as dysuria or polyuria, urinary incontinence, and enuresis. Similarly, Damp–Heat in the Bladder will inhibit Shen’s
–Qi, with subsequent failed Bladder control, presents as dysuria or polyuria, urinary incontinence, and enuresis. Similarly, Damp–Heat in the Bladder will inhibit Shen’s 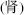 ability to transform Qi, causing dysfunctional urination, stomachache, and lumbago.
ability to transform Qi, causing dysfunctional urination, stomachache, and lumbago.
(2) TCM also notes a similar relationship between Shen and San Jiao
San Jiao transports water to Shen 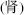 as well as influences Bladder processing.
as well as influences Bladder processing.

