The selection and combined usage of two or more types of medicinal materials based on the different symptoms and medicine nature is called compatibility of medicines (peiwu 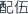 ).
).
Throughpeiwu 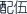 , different curative effects will be induced. Some curative effects are strengthened while others have counteractive effects which reduce the toxicity or side effects of medicines. Such different effects are collectively called seven emotions (qi qing
, different curative effects will be induced. Some curative effects are strengthened while others have counteractive effects which reduce the toxicity or side effects of medicines. Such different effects are collectively called seven emotions (qi qing 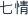 ), namely using a single herb (danxing
), namely using a single herb (danxing 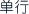 ), (mutual reinforcement (xiangxu
), (mutual reinforcement (xiangxu  ), mutual assistance (xiangshi
), mutual assistance (xiangshi  ), mutual restriction (xiangwei
), mutual restriction (xiangwei  ), neutralisation (xiangsha
), neutralisation (xiangsha  , mutual inhibition (xiangwu
, mutual inhibition (xiangwu  ) and incompatibility (xiangfan
) and incompatibility (xiangfan  ).
).
Among the “seven emotions”,xiangxu  andxiangshi
andxiangshi  can enhance the curative effects of the original medicines, a principle ofpeiwu
can enhance the curative effects of the original medicines, a principle ofpeiwu  which people abide by;xiangwei
which people abide by;xiangwei  andxiangsha
andxiangsha  reduce and remove toxic and side effects to ensure that medicines are safe for use;xiangwu
reduce and remove toxic and side effects to ensure that medicines are safe for use;xiangwu  andxiangfan
andxiangfan  offset or reduce the effects of another medicine, or produce toxic reactions or poison and side effects. These are taboos in the application ofpeiwu
offset or reduce the effects of another medicine, or produce toxic reactions or poison and side effects. These are taboos in the application ofpeiwu 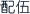 and should be avoided as far as is possible.
and should be avoided as far as is possible.
Fast facts
The “seven emotions” of Chinese medicines
Using a single herb (danxing 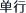 ): the use of a single herb to independently treat the illness. E.g. pueraria root can be used alone to treat sicknesses such as migraine headache, high blood pressure, coronary heart disease and abnormal heart rhythm Mutual reinforcement (xiangxu
): the use of a single herb to independently treat the illness. E.g. pueraria root can be used alone to treat sicknesses such as migraine headache, high blood pressure, coronary heart disease and abnormal heart rhythm Mutual reinforcement (xiangxu  ): two ingredients with similar properties and effects are used in combination to reinforce each other’s original effects. Mutual assistance (xiangshi
): two ingredients with similar properties and effects are used in combination to reinforce each other’s original effects. Mutual assistance (xiangshi  ): a principal medicine is used while the rest play a subsidiary role to reinforce the action of the principal medicine. Mutual restriction (xiangwei
): a principal medicine is used while the rest play a subsidiary role to reinforce the action of the principal medicine. Mutual restriction (xiangwei  ): the toxic and side effects of a medicine are restricted by another medicine. They can also be weakened and neutralised. Neutralisation (xiangsha
): the toxic and side effects of a medicine are restricted by another medicine. They can also be weakened and neutralised. Neutralisation (xiangsha  ): the property of a medicine neutralises the toxicity and side effects of another medicine. Mutual inhibition (xiangwu
): the property of a medicine neutralises the toxicity and side effects of another medicine. Mutual inhibition (xiangwu  ): the effects of a medicine are weakened by another medicine. Incompatibility (xiangfan
): the effects of a medicine are weakened by another medicine. Incompatibility (xiangfan  ): the toxic reactions and side effects are produced or enhanced when two incompatible medicines are used in combination.
): the toxic reactions and side effects are produced or enhanced when two incompatible medicines are used in combination.

