- The Introduction of Hypochondriac Pain
- The Etiology of Hypochondriac Pain
- The Pathology of Hypochondriac Pain
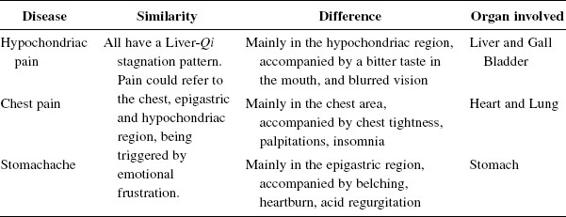
- How to Diagnose and differentiate Hypochondriac Pain(see Table 12)
- The Treatment of Hypochondriac Pain
- Principle of treatment
- Acupuncture
- Auricular acupuncture
- Plum blossom needle
- Bleeding cupping
- Scalp acupuncture
- Electroacupuncture
- Suggestions
The Introduction of Hypochondriac Pain
Definition
Pain on one or both sides of the ribcage is called hypochondriac pain.
Clinical features
Besides hypochondriac pain, there are symptoms associated with the Liver and Gall Bladder, such as a bitter taste in the mouth, jaundice, dislike of greasy food, nausea, and poor appetite.
Corresponding diseases in CWM
- Acute or chronic hepatitis
- Inflammation of the gall bladder
- Gallstones
- Intercostal neuralgia (nerve pain)
- Pleurisy
- Chest trauma
- Costochondritis
The Etiology of Hypochondriac Pain
Emotional frustration
Leads to Qi stasis → Blood stasis → blockage of meridians/failure to nourish the Liver Meridian → hypochondriac pain.
External trauma
Damages the collaterals → Blood stasis → blockage of the meridians/failure to nourish the Liver Meridian → hypochondriac pain.
Irregular diet/invasion of dampness
Retention of Damp-Heat in the Liver (blockage of the meridians/failure to nourish the Liver Meridian hypochondriac pain).
Long-term illness/weak constitution/overstrain
Damages Jing and Blood (Liver-Yin deficiency) → failure to nourish the Liver Meridian/blockage of the meridians → hypochondriac pain.
The Pathology of Hypochondriac Pain
- The chief organs are the Liver and Gall Bladder. It is associated with the Spleen, Stomach, and Kidney.
- The chief pathology is Liver-Qi stagnation leading to disharmony of the meridian.
- It is usually excessive in the early stage: Qi stagnation, Blood stasis, or Damp-Heat. Chronic cases turn into deficiency: Essence and Blood deficiency fail to nourish the Liver Meridian. There is inter-transformation between excess and deficiency: Lingering excess damages Zheng Qi, leading to deficiency. Deficiency may create excess. For example, Qi stagnation can lead to Blood stasis, and Blood stasis can create Blood deficiency; Yin deficiency can create Heat and Blood stasis. If deficiency is present it is easy to catch EFPs or be damaged by food, leading to a mixed pattern.
How to Diagnose and differentiate Hypochondriac Pain(see Table 12)
Key points for pattern differentiation
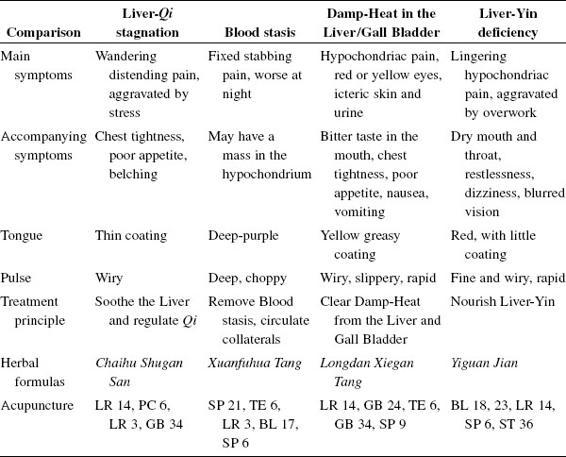
(1)Qi stagnation
- Distending, wandering pain.
- Intermittent.
- Aggravated by emotions.
Basic points: LR 14, GB 24, 34, TE 6, BL 18, 19.
(2)Blood stasis
- Stabbing, fixed, constant pain.
- Worse at night.
(3)Deficiency
- Mild or dull pain.
- Pain with preference for touch.
(4)Excess
- Severe pain.
- Pain with dislike of touch or pressure.
The Treatment of Hypochondriac Pain
Principle of treatment
- Unblock the meridian.
- If excess, regulate Qi, move Blood, clear Heat, transform Dampness.
- If deficiency, nourish Yin and Blood, soothe the Liver, regulate Qi.
Acupuncture
(1)Main points
- LR 3, 14
- GB 24, 34
- TE 6
- BL 18, 19
(2)Liver-Qi stagnation
- LR 3, 14
- PC 6
- GB 34
- Mostly Hand and Foot Jueyin Meridians
- Even method
(3)Blood stasis
- SP 6, 21
- TE 6
- LR 3
- BL 17
- Mostly LR and TE Meridians
- Reducing technique
(4)Damp-Heat in LR/GB
- LR 14
- GB 24, 34
- TE6
- SP9
- Mostly TE, GB, and SP Meridians
- Reducing technique
(5)Liver-Yin deficiency
- BL 18, 23
- LR 14
- SP 6
- ST 36
- Mostly LR, SP, Back Shu points
- Tonifying technique
Fever → LI 4, 11.
Poor appetite → CV 12, 13.
Vomiting → PC 6, ST 36.
Auricular acupuncture
- Liver
- Gall Bladder
- Shenmen
- Chest
- Brain
Plum blossom needle
- Use on Ashi points, Back Shu points, and Huatuojiaji points until the back becomes red.
Bleeding cupping
- Useful if Blood stasis or Heat pathology is present.
Scalp acupuncture
- Sensory line.
- Treat the opposite side of pain.
Electroacupuncture
- Intermittent or mixed wave.
Suggestions
- Exercises are useful for building Zheng Qi and preventing trauma.
- Regulate the emotions.
- Regulate the diet (fresh, easily digested food; no spicy, greasy, raw, or cold food).
- Light massage of hypochondrium can be helpful.
- Get Western medical diagnosis.
- Use on Ashi points, Back Shu points, and Huatuojiaji points until the back becomes red.
Bleeding cupping
- Useful if Blood stasis or Heat pathology is present.
Scalp acupuncture
- Sensory line.
- Treat the opposite side of pain.
Electroacupuncture
- Intermittent or mixed wave.
Suggestions
- Exercises are useful for building Zheng Qi and preventing trauma.
- Regulate the emotions.
- Regulate the diet (fresh, easily digested food; no spicy, greasy, raw, or cold food).
- Light massage of hypochondrium can be helpful.
- Get Western medical diagnosis.
- Sensory line.
- Treat the opposite side of pain.

