The Introduction of Vomiting
Definition
Vomiting means to eject the contents of the stomach through the esophagus and out of the mouth. It is a common symptom in digestive disorders, resulting from the failure of Stomach-Qi to descend. It is called Ou (Vomiting with sound) or Tou (Vomiting without sound) in TCM.
Corresponding diseases in CWM
- Stomach ulcer
- Gastric neurosis
- Gastritis
- Cardiac spasm
- Pyloric spasm
- Blockage of pylorus
- Hepatitis
- Pancreatitis
- Cholecystitis
- Cerebral problems
- Migraine headache
The Etiology of Vomiting
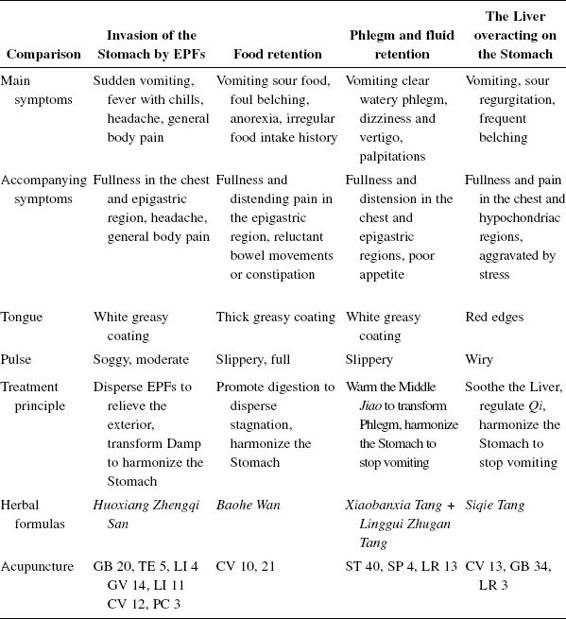
- Invasion of the Stomach by EPFs, especially Dampness, Summer Heat, Wind, and Cold.
- Emotional factors (the Stomach is the most emotional organ in the body).
- Emotional frustration → Liver-Qi stagnation → rebellion of Stomach-Qi.
- Overthinking → damages the Spleen → retention of food and production of Phlegm.
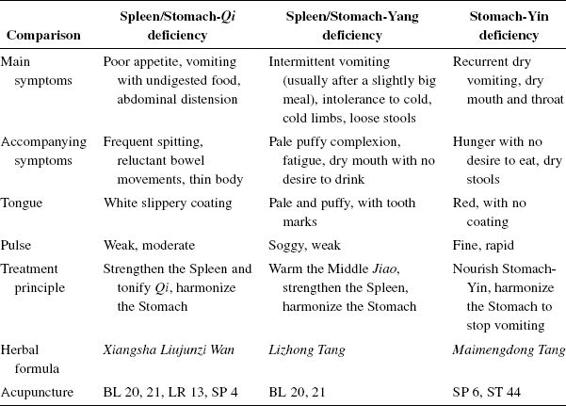
- Improper diet → consuming too much raw, cold, spicy, greasy, or unclean food or alcohol → damages the Stomach — leads to Yang/Qi deficiency in the Middle Jiao or Stomach-Yin deficiency → rebellion of Stomach-Qi.
- A constitutionally weak Spleen and Stomach, or long-term illness, damages the Spleen and Stomach, which then fail to transform and transport food.
The Pathology of Vomiting
Chief Pathology
- Emotional frustration → Liver-Qi stagnation → rebellion of Stomach-Qi.
- Overthinking → damages the Spleen → retention of food and production of Phlegm.
Rebellion of Stomach-Qi because of disharmony of the Stomach.
Organs involved
The chief organ is the Stomach, but it is also related to the Spleen, Liver, and Gall Bladder.
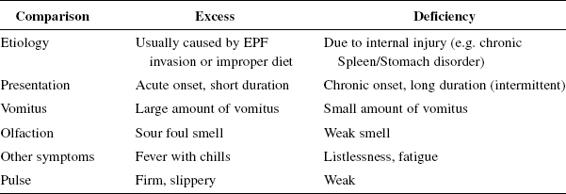
How to Diagnose and differentiate Vomiting(see Table 17)
Differentiation based on vomitus
- Sour with a strong smell → food retention.
- Bitter, yellow water → Gall Bladder-Heat overacting on the Stomach.
Basic points: PC 6, CV 12, ST 36.
Basic points: PC 6, CV 12, ST 36.
- Sour, green water → Liver-Heat overacting on the Stomach.
- Vomitus with turbid Phlegm and bubbles → Phlegm or retained fluids blocking the Middle Jiao.
- Vomitus with clear water → Stomach deficiency or parasites.
- Sticky vomitus that is difficult to remove → Stomach-Yin deficiency.
The Treatment of Vomiting
Principle of treatment
(1)Branch treatment
- Harmonize the Stomach, and descend Stomach-Qi to stop vomiting.
(2)Root treatment
- Remove the pathogenic factor(s).
- Transform Phlegm.
- Soothe the Liver.
- Strengthen the Spleen.
- Tonify Qi.
- Nourish Yin.
Acupuncture
(1)Primary points
- PC 6, CV 12, ST 36
(2)Modifications
Cold → Taiyin Meridians.
Heat → Shaoyang Meridians.
Food retention → reducing on CV and Foot Yangming Meridians.
Phlegm → use moxa on Foot Taiyin and Foot Yangming Meridians.
Liver overacting on SP/ST → reducing on Liver, Gall Bladder, and Stomach Meridians.
Spleen/Stomach-Qi Deficiency → moxa, cupping.
Distension → CV 6.
Borborygmus → BL 20 (Back Shu of the Spleen), BL 25 (Back Shu of the Large Intestine).
Regurgitation → PC 6, SP 4.
Dry vomit → moxa on PC 5 (7 units).
Dizziness → GB 20.
Very yellow vomitus → GB 40.
Auricular therapy
- Stomach
- Shenmen
- Occipital
- Sympathetic
- Subcortex
- Esophagus
Use three points each time, with strong stimulation or ear seeds.
Herbal external application
- Especially good for Cold-type vomiting. Combine the herbal function with the needle function.
- Wu Zhu Yu — belongs to the Warm interior category. Grind into a powder and then mix with vinegar/water and place on KI 1. The effect occurs 1–4 h later. Also good for children with malnutrition.
- Herbal medicine — see chart below.
Suggestions
Acupuncture is very effective for excess-type vomiting.
- For air, car, or sea sickness, press on PC 6 or place ginger juice on the point.
- Avoid invasions by EPFs, especially dampness and summer heat.
- Regulate emotions to prevent the Liver from overacting on the Stomach.
- For Spleen/Stomach deficiency, avoid eating too much all at once and avoid cold, raw food. For Stomach-Heat, avoid spicy and fried food, and alcohol, and smoking.
- For problems with herbal medications, avoid herbals with a fishy odor. Choose pleasant smelling herbals. Cook smaller amounts of concentrated bitter herbs more frequently. For severe vomiting, get the patient to chew ginger and then drink the tea. For Stomach-Heat, the herbal medication will be vomited if it is too cold in nature.

